NMN And Immune System: Does NMN Boost The Immune System?

Yes, studies show that NMN helps T cells and natural killer cells respond to threats more effectively, reduces harmful inflammation, and strengthens resilience against infections and age-related decline.
Scientists are uncovering how NMN may be the missing link between energy, immunity, and longevity — but what does the full picture reveal? Let’s discover more about NMN and immunity.
But First, What Is NMN?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a direct precursor of a molecule called NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). NAD+ is essential for turning food into energy and regulating many different processes inside cells, including DNA repair and managing oxidative stress.
As we age, NAD+ levels naturally decline, which is associated with many different age-related conditions, including weakened immunity and chronic inflammation. Therefore, scientists are now investigating whether restoring NAD+ using NMN can help immune cells stay energized and responsive even as you age.
Does NMN Boost The Immune System?
Yes, there’s some evidence that NMN might be able to activate the immune response, especially in immunocompromised people.
People who have HIV are usually immunocompromised. This means that their immune system is weakened. However, a study found that NMN enhances immune function by increasing NAD+ levels in HIV patients.
This is very promising because it suggests that even when someone’s immune system isn’t working the way it should, NMN might be able to rescue it.
Does NMN Reduce Inflammation?
Yes, there’s significant evidence that NMN reduces inflammation.
Chronic inflammation, sometimes called “inflammaging,” is one of the main reasons immunity weakens with age. However, a recent study found that NMN reduces inflammation in human cells, by decreasing the levels of cytokines such as IL-6.
Your immune system releases cytokines to raise alarms at the site of infection or injury. Elevated cytokine levels usually drive inflammation. By repressing the production of a major cytokine, IL-6, NMN actively demonstrates its potential as a potent anti-inflammatory compound.
Can NMN Help With Autoimmune Conditions?
There’s some evidence that NMN might be able to offer some protection in mice models of multiple sclerosis. However, these studies used NAD+ directly, and not the precursor NMN.
Researchers found that NAD+ can be used both preventatively and therapeutically in mice models of multiple sclerosis (MS). Since NMN is a precursor of NAD+, it stands to reason that NMN might offer similar beneficial effects in MS.
In multiple sclerosis (MS), your immune system attacks your neurons, making it a complicated autoimmune disorder. In MS, immune cells strip away the protective sheath around neurons, called myelin. However, scientists discovered that administering NAD⁺ increased the number of cells that produce IL-10, an anti-inflammatory cytokine.
This finding directly connects to NMN’s role in inflammation. Scientists still need to conduct more research in human patients before they can establish NMN’s role in autoimmunity.
What Role Does NMN Play In Inflammaging?
There’s some evidence that NMN may regulate and lower inflammaging. However, we need more clinical research in humans before establishing any concrete effect.
As people age, immune cells lose efficiency. This leads to slower wound healing, higher infection risk, and more inflammation. NAD+ decline is inversely associated with inflammaging. However, studies show NMN supplementation can:
-
Reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines that may be causing inflammaging.
-
Improve clearance of senescent cells (old, dysfunctional cells that trigger inflammation)
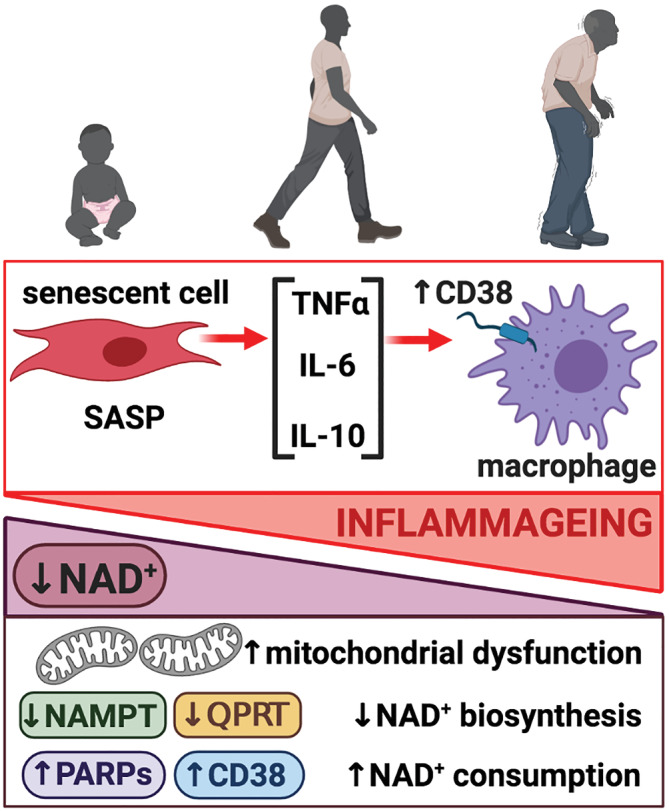
Figure taken from Navarro et al., 2022.
In this way, NMN helps counter immunosenescence — the gradual deterioration of immune function with age.
Is NMN Safe For Humans?
Yes. Clinical studies so far show that humans tolerate NMN safely, even at higher doses. However, researchers have not yet established its long-term effects through large-scale clinical trials.
NMN doses for humans generally start somewhere between 100-250 mg/day, and have been studied up to 2000 mg/day.
NMN does not cure everything. You should view it as part of a broader wellness strategy that includes balanced nutrition, exercise, and regular medical care.
Final Thoughts: NMN and Immune System
The link between NMN and the immune system is backed by growing scientific evidence. By replenishing NAD+, NMN supports energy production in immune cells, reduces chronic inflammation, and helps balance immune activation and even autoimmune conditions.
If you are serious about supporting your immune health and ageing gracefully, consider adding NMN as part of your wellness routine.
Shop Ultra Pure NMN™ today to fuel your immune defenses with the highest quality NMN available.
References
-
Shade C. (2020). The Science Behind NMN-A Stable, Reliable NAD+Activator and Anti-Aging Molecule. Integrative medicine (Encinitas, Calif.), 19(1), 12–14.
-
Mo, Y., Yue, M., Yim, L. Y., Zhou, R., Yu, C., Peng, Q., Zhou, Y., Luk, T. Y., Lui, G. C., Huang, H., Lim, C. Y. H., Wang, H., Liu, L., Sun, H., Wang, J., Song, Y., & Chen, Z. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide impacts HIV-1 infection by modulating immune activation in T lymphocytes and humanized mice. EBioMedicine, 98, 104877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104877
-
Franceschi, C., Garagnani, P., Parini, P., Giuliani, C., & Santoro, A. (2018). Inflammaging: a new immune-metabolic viewpoint for age-related diseases. Nature reviews. Endocrinology, 14(10), 576–590. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0059-4
-
Sano, H., Kratz, A., Nishino, T., Imamura, H., Yoshida, Y., Shimizu, N., Kitano, H., & Yachie, A. (2023). Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) alleviates the poly(I:C)-induced inflammatory response in human primary cell cultures. Scientific reports, 13(1), 11765. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-38762-x
-
Navarro, M. N., Gómez de Las Heras, M. M., & Mittelbrunn, M. (2022). Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism in the immune response, autoimmunity and inflammageing. British journal of pharmacology, 179(9), 1839–1856. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.15477
-
Wang, H., Sun, Y., Pi, C., Yu, X., Gao, X., Zhang, C., Sun, H., Zhang, H., Shi, Y., & He, X. (2022). Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Supplementation Improves Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Rescues Cellular Senescence by NAD+/Sirt3 Pathway in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. International journal of molecular sciences, 23(23), 14739. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232314739
-
Pencina, K. M., Valderrabano, R., Wipper, B., Orkaby, A. R., Reid, K. F., Storer, T., Lin, A. P., Merugumala, S., Wilson, L., Latham, N., Ghattas-Puylara, C., Ozimek, N. E., Cheng, M., Bhargava, A., Memish-Beleva, Y., Lawney, B., Lavu, S., Swain, P. M., Apte, R. S., Sinclair, D. A., … Bhasin, S. (2023). Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Augmentation in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Physiologic Study. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 108(8), 1968–1980. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgad027


