NMN And Cardiovascular Health: Clinical Insights & Research | HealthspanX
Is NMN Good For Your Heart? Exploring NMN and Cardiovascular Health
NMN and cardiovascular health are closely linked through NMN’s ability to restore NAD⁺ levels. It enhances mitochondrial function, reduces inflammation, and supports vascular integrity. This is central to preventing heart disease and age-related cardiac decline.
With heart disease remaining the number one cause of death in the U.S., many are exploring ways to protect their hearts beyond just medication. One molecule gaining attention in the scientific community is nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN).
Molecular and cellular cardiology provides the scientific foundation for understanding how NMN can protect mitochondrial function within heart cells and prevent heart failure.
Figure taken from CDC, Mortality in the United States, 2023.
If you are curious about the connection between NMN and cardiovascular health, you have come to the right place. In this guide, we will explore how NMN might be able to help protect your heart, diving into molecular pathways, preclinical studies, and early clinical findings.
Previous studies have explored the relationship between NMN, NAD+ levels, and cardiovascular health, establishing a strong scientific background for ongoing research in this area.
So let’s start our scientific voyage and discover the wonders of NMN in cardiovascular health!
What Is NMN?
NMN is a direct precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). NAD+ is a coenzyme essential for redox reactions, mitochondrial energy production, DNA repair, and epigenetic regulation.
NAD+ levels reduce during aging. This is linked to many different diseases and disorders, including cardiovascular problems. Therefore, scientists are trying to understand whether replenishing NAD+ levels through NMN supplementation can protect against heart problems.
And current research is exciting!
Mitochondrial Function And Heart Health
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of heart cells, generating the energy needed for every heartbeat. When mitochondrial function falters—a phenomenon known as mitochondrial dysfunction—the heart’s ability to pump efficiently is compromised, paving the way for cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure and cardiac dysfunction. Maintaining cardiac mitochondrial homeostasis is therefore essential for lifelong cardiovascular health.
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) has emerged as a promising molecule for supporting mitochondrial health. NMN supplementation boosts levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a critical coenzyme that fuels mitochondrial energy production and regulates cellular repair processes. As we age, NAD+ levels naturally decline, contributing to age-associated physiological decline and increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Research shows that NMN treatment can restore NAD+ levels, helping to preserve mitochondrial homeostasis in heart tissue. This restoration is linked to reduced mitochondrial protein acetylation—a marker of mitochondrial stress—and improved cardiac function. By supporting the heart’s energy metabolism, NMN administration helps protect against the cellular damage that leads to heart failure and other cardiovascular diseases.

Clinical trials and preclinical studies have demonstrated that NMN intake can lower blood pressure, enhance vascular function, and reduce arterial stiffness. These benefits are partly due to NMN’s ability to decrease reactive oxygen species production and regulate oxidative stress, both of which are major contributors to vascular dysfunction and significant cell death in cardiac tissue.
Importantly, NMN’s positive effects extend beyond the heart, offering potential benefits for overall metabolic health. By improving mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, NMN may help counteract metabolic disorders that often accompany cardiovascular disease.
Can NMN Protect Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury?
Yes, and this is one of the most well-characterized areas of NMN's cardiovascular research.
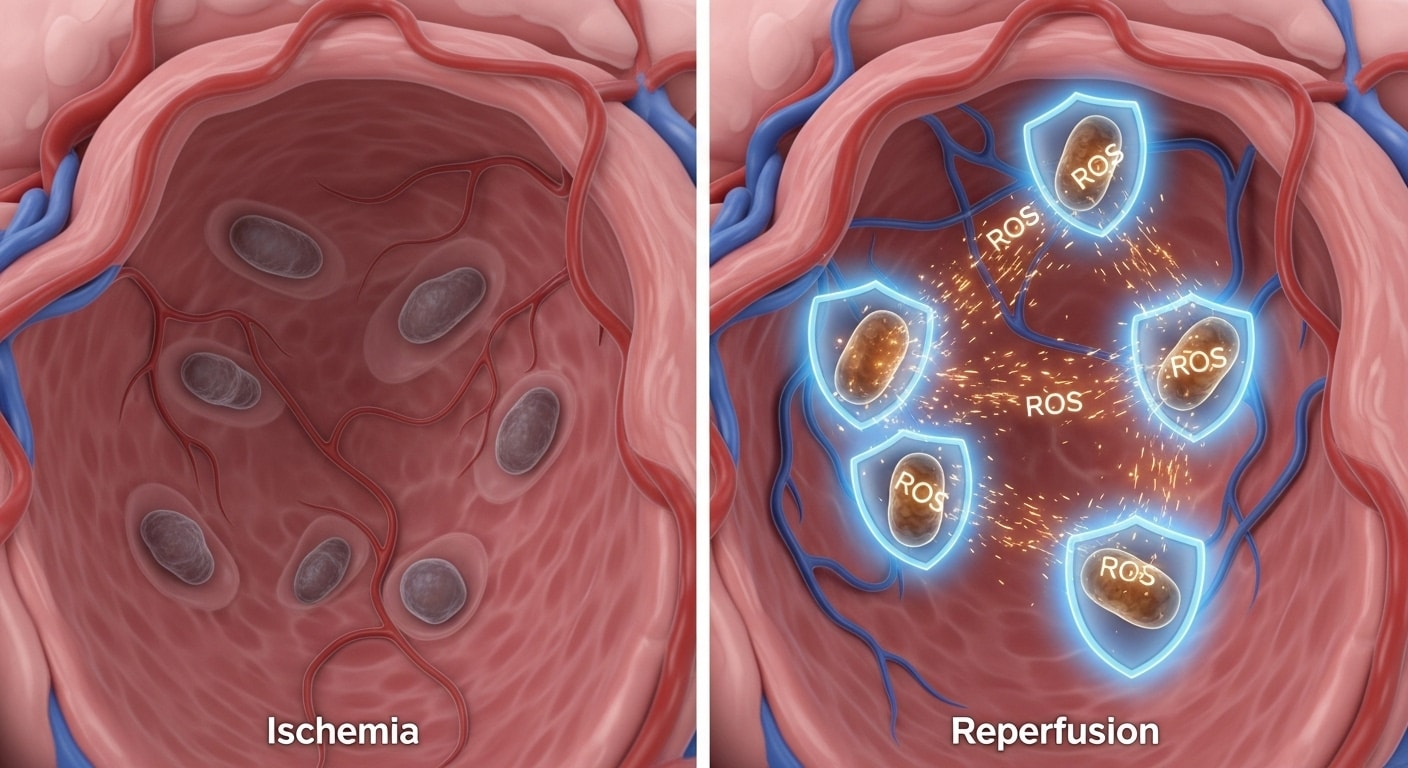
What Is Ischemia/Reperfusion (I/R) Injury?
During ischemia, blood flow to the heart muscle is restricted. This can damage tissues. Now you may think that if the blockage is causing the problem, restoring blood flow should fix the damage, right? WRONG.
Restoring the blood flow (reperfusion) to ischemic tissues can cause even more damage. That's because the reintroduced blood leads to a burst of oxidative stress and calcium overload, This complete phenomenon called ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury.
How Does NMN Protect Against (I/R) Injury?
In animal models, NMN treatment increased NAD+ levels in heart cells, activated SIRT1, and preserved mitochondrial membrane potential.
Remember that a chunk of I/R injury is caused by oxidative stress. Oxidative stress is caused by reactive oxidative species (ROS). And to control ROS, we need antioxidants. One of these antioxidants is SIRT1. However, SIRT1 uses NAD+ as its payment for its antioxidant services.
Here's how it works:
-
NMN supplementation increases the level of NAD+ in heart muscles.
-
Increased NAD+ allows SIRT1 to exert its antioxidant effects.
-
However, SIRT1 needs another player FOXO1 to partially create a protective effect.
-
So SIRT1 activates FOXO1 and together the two of them help in creating an antioxidant barrier against oxidative stress.
-
In addition to that, SIRT1 also lowers apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cardiac tissue in response to I/R injury.
How Does NMN Impact Atherosclerosis And Vascular Aging?
NMN reduces arterial plaque and vascular inflammation while improving vessel stability, offering protection against atherosclerosis and vascular aging.
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque inside arteries. It is not just a cholesterol issue, but also an inflammatory disease. In a 2024 preclinical study, scientists decided to see if NMN could help tackle atherosclerotic problems.
They fed mice a high-fat diet to capture the same disease progression route as you would see in humans. And then they gave some of the mice 500 mg/kg NMN daily for six days a week. The rest of the mice didn't receive NMN. This experiment ran for 8 weeks.
At the end of the 8 weeks, the team inspected the blood vessels of these mice. They found that the mice that were given NMN had 36% less plaques, compared to the other mice. And that the accumulation of fat in blood vessels also reduced by 43%. This is really exciting!
It suggests that NMN may be able to protect against atherosclerotic problems, or maybe even treat them!
Does NMN Prevent Plaque Breakage In Atherosclerosis?
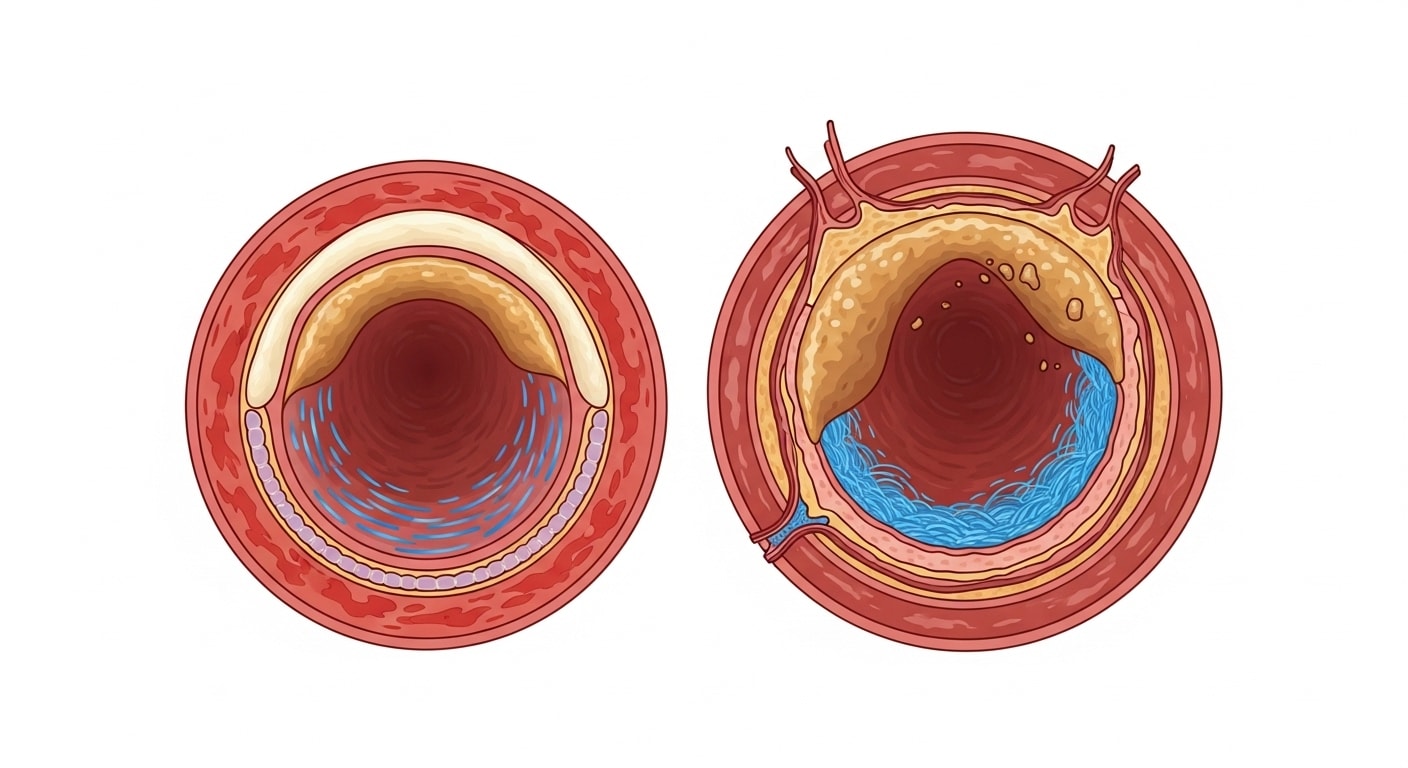
Yes, NMN prevents plaques from breaking off and traveling down the bloodstream.
Another big problem with plaques is that they can sometimes break off and start traveling down the blood vessels. Then they can stick to random places, start new plaques, or even block certain blood vessels. It can be really dangerous for vessels close to the heart and lead to acute cardiovascular problems such as heart attacks.
However, the scientists found that the plaques in the mice that were given NMN were more stable! They had 51% more collagen. Collagen is a protein that helps in forming connective tissue. This suggests that the plaques in NMN mice are more likely to remain intact and not break off.
Together all of this is super exciting for cardiovascular scientists. And it paves a new road for therapies that protect the heart.
NMN Treatment In Heart Failure And Cardiomyopathy
NMN improves cardiac function in animal models of heart failure by restoring NAD⁺ levels and enhancing mitochondrial dynamics.
Cardiac failure means the heart becomes weak and cannot pump blood as well as it should. One reason this happens is that the energy-making parts of heart cells—called mitochondria—start to break down. They become small, scattered, and don’t make enough fuel (ATP). This makes it harder for the heart to beat properly.
In certain studies with mice that had serious heart problems, NMN helped fix these energy problems. In these animal studies, the administration of NMN was used as a treatment method to improve mitochondrial health and prevent heart failure, often through direct injection or short-term therapy. Previous studies have demonstrated a strong relationship between mitochondrial dysfunction, NAD+ depletion, and the development of heart failure. Here’s how it did that:
-
NMN gives mitochondria more NAD+, a molecule they need to produce energy (ATP).
-
NMN activated a helper protein called SIRT3, which turned on key energy enzymes. Additionally, SIRT3 is an antioxidant which helps in protecting the heart muscles against oxidative stress.
Because of these changes, the mice were protected against heart failure. This is promising because currently it’s only been tested in mice. However, if similar results happen in people, it could help us find more preventative therapies for heart attacks.
Can NMN Supplementation Improve Endothelial Function And Blood Pressure?
Clinical research shows that NMN supplementation can significantly lower both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in adults—especially those with mild hypertension or obesity. High blood pressure is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and NMN’s ability to lower blood pressure may help mitigate this risk.
Clinical Trials On NMN Administration For Blood Pressure
Here are some of the key findings about NMN’s use in hypertension:
-
In a 2023 trial (Sun Yat-sen University), adults with mild hypertension took 800 mg/day of NMN for six weeks. The oral administration of NMN led to a significant drop in systolic blood pressure, compared to people who only made lifestyle modifications (such as eating healthy or working out).
-
A Harvard-led randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial gave 2,000 mg of NMN per day to overweight adults. They noticed a significant reduction in diastolic blood pressure, and reductions in LDL and body weight. No adverse effects were reported, even at this high dose.
Is NMN Safe For Long-Term Use In Heart Patients?
Current research on NMN in heart function has been limited to animal models of heart failure phenotype. We don't know if it's safe for long-term use in heart patients. However, clinical studies in hypertensive adults suggests that NMN is safe to use (even at high doses of 2,000 mg/day).
Phase I trials in humans (UMIN000021309) suggest NMN is safe and well tolerated at doses ranging from 250 mg to 500 mg daily.
Still, caution is warranted! Please always consult your healthcare provider before taking NMN, if you are on any form of medication.
Final Thoughts: Is NMN Good For Your Heart? NMN And Cardiovascular Health
From ischemic protection to vascular remodeling and mitochondrial rejuvenation, NMN offers a multi-pathway strategy for supporting heart health at the molecular level.
While further clinical trials are needed to fully understand the long-term impact of NMN supplementation on cardiovascular health, current evidence suggests that NMN administration could be a valuable addition to strategies aimed at preserving heart function and promoting healthy aging.
While most evidence is still preliminary, animal studies show compelling effects across blood pressure regulation, atherosclerosis prevention, and energy balance in heart failure.
NMN's ability to restore NAD+—a central molecule of life and longevity—makes it one of the most promising cardiovascular nutraceuticals available today.
If you are serious about giving your heart a metabolic advantage as you age, consider Ultra Pure NMN™ from HealthspanX! With 99.2% purity, we offer clinical grade NMN - ready to change the way you age for the better?
References
-
Murphy, S. L., Kochanek, K. D., Xu, J. Q., & Arias, E. (2024, December). Mortality in the United States, 2023 (NCHS Data Brief No. 521). National Center for Health Statistics. https://dx.doi.org/10.15620/cdc/170564
-
Deng, H., Ding, D., Ma, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, N., Zhang, C., & Yang, G. (2024). Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: Research Process in Cardiovascular Diseases. International journal of molecular sciences, 25(17), 9526. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25179526
-
Wang, Z., Zhou, S., Hao, Y., Xu, T., An, P., Luo, Y., & Luo, J. (2024). Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against high-fat-diet-induced atherosclerosis in mice and dampens aortic inflammation and oxidative stress. Journal of Functional Foods, 112, 105985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2023.105985
-
Qiu, Y., Xu, S., Chen, X., Wu, X., Zhou, Z., Zhang, J., Tu, Q., Dong, B., Liu, Z., He, J., Zhang, X., Liu, S., Su, C., Huang, H., Xia, W., & Tao, J. (2023). NAD+ exhaustion by CD38 upregulation contributes to blood pressure elevation and vascular damage in hypertension. Signal transduction and targeted therapy, 8(1), 353. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01577-3
-
Pencina, K. M., Valderrabano, R., Wipper, B., Orkaby, A. R., Reid, K. F., Storer, T., Lin, A. P., Merugumala, S., Wilson, L., Latham, N., Ghattas-Puylara, C., Ozimek, N. E., Cheng, M., Bhargava, A., Memish-Beleva, Y., Lawney, B., Lavu, S., Swain, P. M., Apte, R. S., Sinclair, D. A., … Bhasin, S. (2023). Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Augmentation in Overweight or Obese Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Physiologic Study. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism, 108(8), 1968–1980. https://doi.org/10.1210/clinem/dgad027
-
Zhang, R., Shen, Y., Zhou, L., Sangwung, P., Fujioka, H., Zhang, L., & Liao, X. (2017). Short-term administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide preserves cardiac mitochondrial homeostasis and prevents heart failure. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology, 112, 64–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.09.001
-
Klimova, N., Long, A., & Kristian, T. (2019). Nicotinamide mononucleotide alters mitochondrial dynamics by SIRT3-dependent mechanism in male mice. Journal of neuroscience research, 97(8), 975–990. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24397
-
Yang, J., Guo, Q., Feng, X., Liu, Y., & Zhou, Y. (2022). Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cardiovascular Diseases: Potential Targets for Treatment. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 10, 841523. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.841523


